Let us start with the basics of reproduction. As all of you understand, reproduction is the process by which microorganisms make various other microorganisms like themselves. In the human reproductive system, there are 2 kinds of sex cells, that are scientifically known as gametes (GAH-meets), which are involved in the process of sexual reproduction. The male gametes, or sperm, that are the male sex cells as well as the female gamete, the egg, or ova, meet within the woman’s reproductive system. When sperm fertilizes (satisfies) an egg, this fed egg is known as a zygote. The zygote after that goes through a procedure of developing into an embryo as well as expanding right into a fetus.
The male reproductive system and the female reproductive system are both equally needed for recreation. Yet what you require to know is that the woman is the one who nurtures the growing unborn child and has the capacity to provide a youngster right into the world. Ladies are born with a big number of prospective ova (lady intercourse cells, in addition to called egg cells). Nonetheless, it is not until after the start of adolescence, usually around age 12, that those cells are adequately fully grown to maintain life. The cells ripen on a day-to-day basis, nevertheless, the most effective one is laid out monthly up until a girl gets to menopause. Menopause usually begins to evolve among a while of forty-five and 55. If fertilizing and/or implantation does not occur, the system is created to menstruate (the monthly shedding of the uterine lining). In addition, the women’s reproductive system generates women’s sex hormonal agents that preserve the reproductive cycle.
Humans, like various other organisms, pass some character characteristics of themselves to the next generation. We do this via our genes, the unique carriers of human traits. The genes that the moms and dads pass along are what make their kids like them as well as others in their family, but likewise what make each child one-of-a-kind. These genetics originate from the male’s sperm as well as the female’s egg.
Just how much do you find out about the female reproductive system?
The outer part of the female reproductive organ is called the vulva, to put it simply- the covering. The vulva exists between the legs and covers the opening to the vaginal area and various other reproductive organs. The fleshy area located just over the top of the vaginal opening is called the mons pubis. 2 pairs of skin flaps called the labia (which implies lips) surround the genital opening. The clitoris, a little sensory body organ, is located towards the front of the vulva where the folds up of the labia join. Between the labia are openings to the urethra (the canal that lugs pee from the bladder to the beyond the body) and the vaginal canal. When women end up being sexually mature, the outer labia, as well as the mons pubis, are covered by pubic hair.
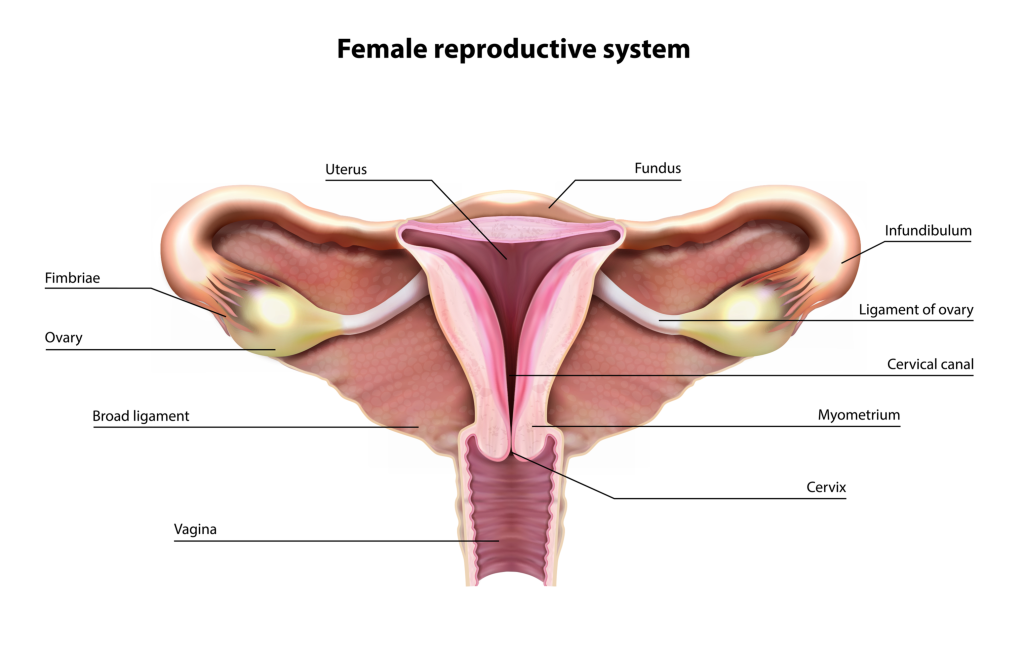
The inner reproductive body organs of a female are the vagina, womb, fallopian tubes, as well as ovaries.
A Vaginal Canal is a muscular tube that absorbs the penis when making love and with it, a youngster leaves the womb throughout childbirth. It is the hollow tube that prolongs from the genital opening to the uterus. Because it has muscle walls, the vaginal area can expand and agree. This ability to come to be wider or narrower allows the vagina to accommodate something as slim as a tampon and as large as an infant. The vaginal canal’s muscle walls are lined with mucous membrane layers, which maintain it secured and moist. The vagina’s purposes are to put the penis throughout intercourse, be the course (birth canal) where the infant leaves the women’s body during childbirth, and the route whereby menstruation blood leaves the body during the duration. A very thin skin-like tissue called the hymen partially covers the opening of the vagina. The hymen typically varies from female to woman. Most women locate that the hymen stretches or splits after the first sexual experience, as well as the hymen can hemorrhage a little (which generally triggers little discomfort). Some women that have had sex do not have much of an adjustment in their hymens, however. And some women’s hymens have already stretched also prior to they having sex. The vaginal area connects with the uterus, or womb, at the cervix (which implies neck). The cervix has strong, thick wall surfaces. The opening of the cervix is little (no larger than a straw), which is why a tampon can never get lost inside a girl’s body. During childbirth, the cervix can broaden to permit a child to pass.
A Uterus, formed like an upside-down pear, with a thick cellular lining and muscular wall surfaces, is an organ that holds and nurtures a growing fetus if an egg becomes properly fed. The womb consists of some of the toughest muscles in the female body. These muscles can increase and contract to support a growing unborn child and afterward aid push the baby out during labor. When a woman is not expecting, the uterus is just about 3 inches (7.5 centimeters) long as well as 2 inches (5 centimeters) large.
The Ovaries – the female gonads, generate eggs. When one matures, it is released down right into a fallopian tube. At the upper corners of the uterus, the fallopian tubes attach the womb to the ovaries. The ovaries are 2 oval-shaped body organs that lie to the top right as well as left of the womb. They generate, save, and launch eggs into the fallopian tubes at the same time called ovulation. The ovary is likewise part of the endocrine system because it generates women hormonal agents such as estrogen and progesterone.
Fallopian tubes are these little tubes that supply eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. This is where an egg waits to be fertilized. There are 2 fallopian tubes, each connected to a side of the uterus. Within each tube is a little passageway no bigger than a sewing needle. At the various other ends of each fallopian tube is a fringed location that resembles a channel. This fringed location twists around the ovary but does not totally connect to it. When the egg pops out of the ovary, it enters the fallopian tube. When an egg goes into the fallopian tube, the tiny hairs on the inner wall of the fallopian tube push the fallopian tube out of the slim flow towards the womb.
Do you understand what occurs after the egg gets fertilized?
When perfectly fed with a person’s sperm, both through sex and artificial insemination, a lady’s egg consists of all the vital products to create youngsters.
If a lady and man make love within numerous days of the female’s ovulation, fertilization can occur. When the male ejaculates (when seminal fluid leaves the penis), a small amount of sperm is transferred right into the vagina. Numerous sperm are in this small amount of seminal fluid, and they “swim” up from the vagina through the cervix as well as womb to meet the egg in the fallopian tube. It takes just one sperm to fertilize the egg.
About 5 to 6 days after the sperm fertilizes the egg, the fed egg (noticeable: zygote) becomes a multi-celled blastocyst. A blastocyst, which is about the same dimension as a pinhead, is a hollow cell with fluid inside. Blastocysts delve right into the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium. The hormone estrogen thickens the inner wall of the womb and enriches the blood. One more hormone released by the ovaries, progesterone, keeps the inner wall of the womb thick with blood, enabling blastocysts to affix to the uterus as well as take in nutrients from it. This process is called porting. When cells from the blastocyst nourish, an additional stage of advancement starts. At the beginning phase, the internal cells create a level circle called the embryo disk, which grows into an infant. The external cells end up being a slim membrane that develops around the child. The cell proliferates countless times, relocates to a brand-new area, and ultimately becomes an embryo.
After about 8 weeks, the embryo is nearly raspberry-sized, but all parts of it (brain and nerves, heart and blood, belly and intestines, muscle mass, as well as skin) are developed. During the fetal period, which lasts from 9 weeks after fertilizing to shipment, cells continue to develop as they multiply, move, as well as adjust. The unborn child then drifts in the amniotic liquid in the amniotic sac. It obtains oxygen and nutrients from the mommy’s blood via the placenta. This disc-shaped structure affixes to the internal layer of the womb and are linked to the unborn child by the umbilical cord. Amniotic liquid and membranes safeguard the unborn child from bumps and shocks to the mom’s body.
Pregnancy lasts an average of 280 days is about 9 months. When the infant awaits birth, its head presses on the cervix, which begins to relax and broaden to prepare for the child to enter and through the vaginal canal. Mucous has formed a plug in the cervix, which currently loosens up. It and amniotic fluid come out through the vaginal area when the mommy’s water breaks.
When the contractions of labor begin, the walls of the uterus agree as they are promoted by the pituitary hormonal agent oxytocin. The contraction creates the cervix to broaden as well as begin to open. Hour’s hereafter dilation, the cervix is completely dilated (opened) for the child to pass through. The baby is pushed out of the womb via the cervix and along the birth canal. Usually, the child’s head comes first. The umbilical cable comes out with the child. It is clamped as well as cut close to the navel after the child is delivered.
The last stage of the birth process includes the shipment of the placenta, which then is called afterbirth. After it has divided from the inner cellular lining of the uterus, tightening of the uterus press it out, in addition to its membranes and fluids.
Read Also:
How Do You Start the Pregnancy Process?
Role Of Male Sex Organs in The Pregnancy Procedure
Disclaimer:
“KareOptions does not have any intention to provide specific medical advice, but rather to provide its users and/ or the general public with information to better understand their health. All content (including text, graphics, images, information, etc.) provided herein is for general informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, care, diagnosis, or treatment. KareOptions makes no representation and assumes no responsibility/ liability for the accuracy of the information, advice, diagnosis, treatment provided herein or on its website. NEVER DISREGARD PROFESSIONAL MEDICAL ADVICE OR DELAY IN SEEKING TREATMENT BECAUSE OF SOMETHING YOU HAVE READ IT HERE OR ACCESSED THROUGH THE KAREOPTIONS WEBSITE.